Facile access to ultrasmall Eu2O3 nanoparticle-functionalized hollow silica nanospheres |
|
|
Hollow inorganic nanospheres have emerged as intriguing materials for applications in drug delivery, catalysis, imaging and photonic crystals, etc. To fully exploit these versatile tiny containers in these applications, it is essential to invent facile ways to install diverse functionality in the sphere interior. As a family of advanced materials, inorganic nanoparticles (NPs), especially with diameters sub-10 nm, have attracted much attention for their unique properties arising from quantum confinement or surface effects. By incorporating electrical, optic and magnetic NPs into hollow spheres, multifunctional nanocomposites can be obtained. We report a promising strategy for the facile synthesis of ultrasmall nanoparticle-functionalized hollow silica nanospheres by using a functional cross-linked organic/inorganic hybrid core, which can be obtained simply through successive spontaneous reactions in water.
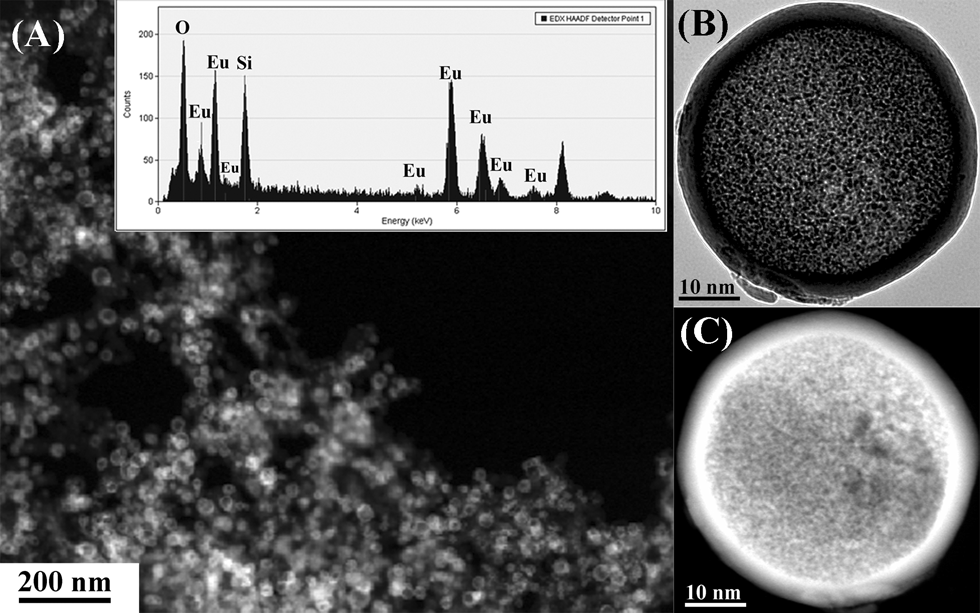
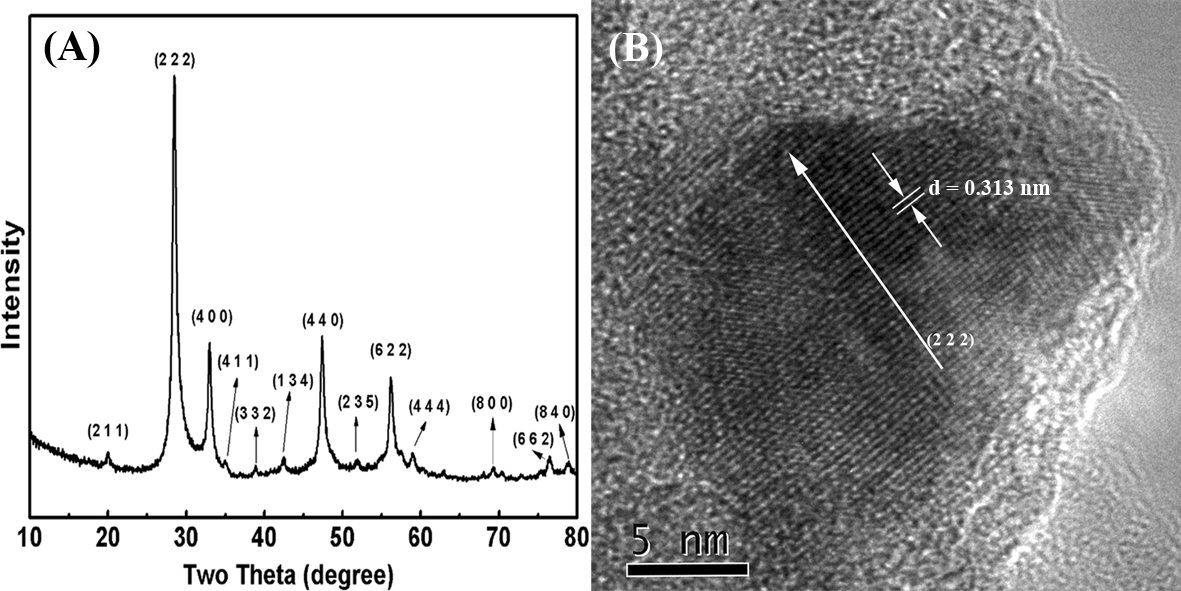
(A) TEM image and EDS spectrum (inset) of Eu2O3@H-SiO2 nanospheres. TEM (B) and STEM (C) image of a single Eu2O3@H-SiO2 nanosphere.
Angular dependence of the observed AMR at 240K,150K,and 70K under magnetic fields of 5T and 9T, respectively, inmeasurement mode B. | |