Exchange bias and its thermal stability in ferromagnetic/antiferromagnetic antidot arrays |
|
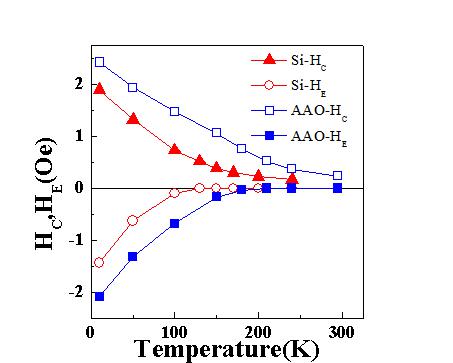
The exchange bias (EB) effect and its thermal stability in nanoscale Co/NiO antidot arrays and sheet films have been investigated. The EB field HE increases with increasing Co thickness (tCo) and reaches a maximum at tCo = 8 nm in the antidot arrays, whereas HE decreases with tCo in the sheet films. Compared with the sheet films, HE in the antidot arrays is either enhanced or decreased, depending on the thickness of the ferromagnetic Co layer, which is due to the three-dimensional effects in the antiferromagnetic NiO and ferromagnetic Co layers caused by the nanopores. A higher thermal stability is observed in the antidot arrays due to the out-of-plane anisotropy constant K1 of the misaligned antiferromagnetic magnetization component.
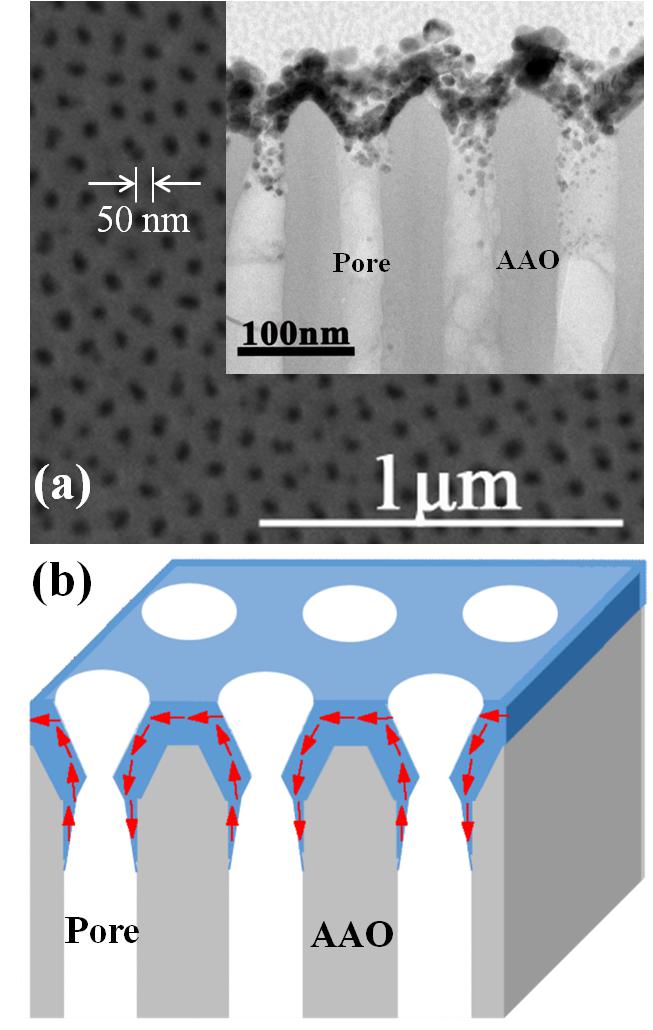
(a) SEM image of Ag(10 nm)/Co(8 nm)/NiO(5 nm)/Ag(5 nm) antidot arrays. (b) Cross section sketch of the antidot arrays, the arrows indicate the magnetization direction of magnetic films.
Temperature dependence of HE and HC for Co(8 nm)/NiO(5 nm) antidot arrays (square) and the continuous films (circle and triangle).
|
|