Abnormal magnetic ordering and ferromagnetism in perovskite ScMnO3 film |
|
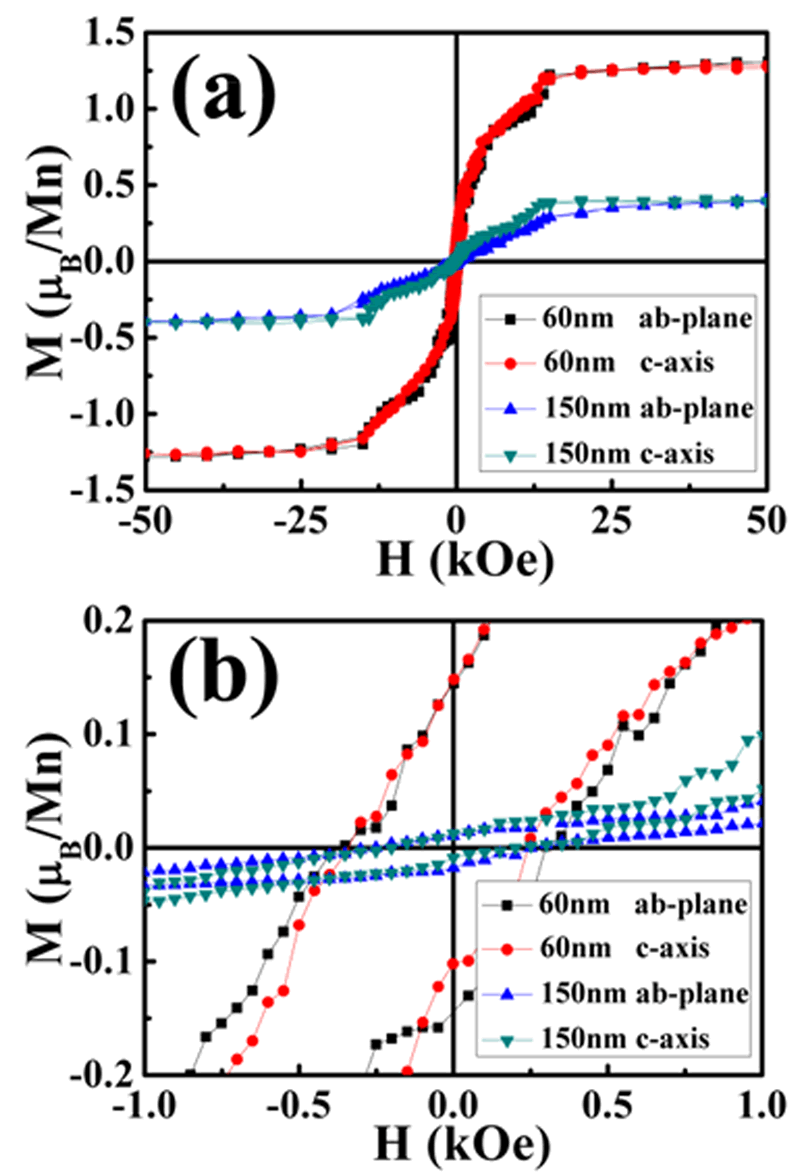
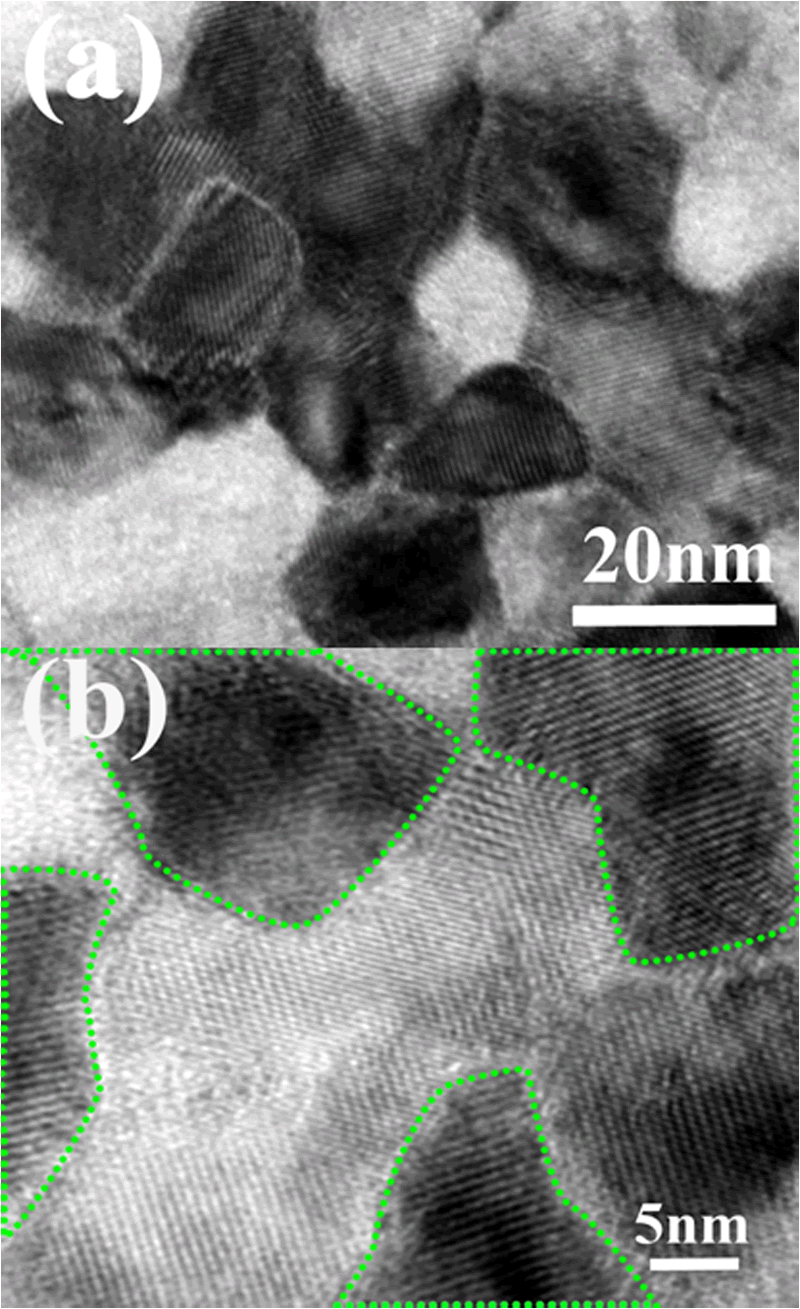
Bulk multiferroic ScMnO3 is the stable hexagonal phase and it is very difficult to prepare its orthorhombic phase even under high pressure. We fabricated the orthorhombic ScMnO3thin film by pulsed laser deposition through suitable substrate LaAlO3and found that nano-scale twin-like domains arenaturally formed in the thin film. Magnetic properties of the orthorhombic ScMnO3 thin films show that, besides normal antiferromagnetic ordering at 47 K, an anomalous magnetic transition occurs at 27 K for 60 nm film and at 36 K for 150 nm film only along the c-axis, which is absent in the ab-plane. Moreover, the second magnetic transition for both films is suppressed when the applied field increases from 1 kOe to 10 kOe. In addition, the ferromagnetism shows up in both films at 10 K and saturation magnetization increases dramatically in 60 nm film compared with 150 nm film. We propose that the second magnetic transition might be more of lattice strain effect and also related to magnetism-induced ferroelectric polarization in orthorhombic RMnO3 thin films, low-temperature ferromagnetic properties in our films originate from the nano-scale twin-like domain structure.
Fig3.(a) The magnetic field dependent magnetization of 60 nm and 150 nm ScMnO3 films along c-axis and in ab plane at10 K. (b) Enlarged low field region of the curves in (a).
Fig. 3. (a) The bright field plane-view TEM image of 60 nm ScMnO<sub>3</sub> film. (b) The high resolution TEM image of the same patch.
|
|